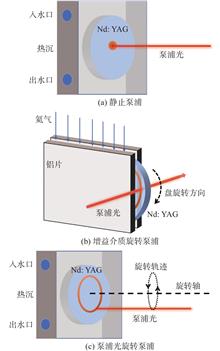
Thermal management in solid-state lasers is still a challenge in the development of high-energy laser systems. Introducing relative motion between the pump beam and the gain medium in the laser system is an efficient thermal management scheme. The temperature distribution of Nd∶YAG crystal was analyzed by means of finite element numerical simulation for static pumping, rotating gain medium pumping and pump-beam rotating pumping. Rotated at 800 r/min with standard heat-sinking cooling the disk temperature increased by only 16 ℃ reaching a maximum temperature of ~36 ℃, which is much lower than ~142 ℃ at static pumping. Experimentally, we designed and demonstrated a Nd∶YAG laser with the extracavity rotatory pumping, and obtained a 12.2 W output of 1064 nm with a slope efficiency of 37.2%, which is greater than the 35.1% at static pumping. The experimental results were coinciding with the theoretical simulation. The study shows that the solid state laser with extracavity rotatory pumping displays greatly enhanced thermal control.
To increase the light efficiency of laser light sources and further achieve long-distance illumination, a scheme based on combining light technology can be used to design a variable focus laser searchlight. Using the method of arranging multiple blue light LDs into an array and utilizing the light recovery technology of the glass reflector bowl, the optical path design of the laser searchlight was carried out. Simultaneously using a dichroic chip to control the divergence angle, variable focus control of the laser searchlight was achieved. Measure the luminous flux output by the laser module at a current of 1 A. After calculation, the total luminous flux emitted from the fluorescent ceramic chip was approximately 730 lm. In addition, changing the scattering characteristics of the uniform light sheet could achieve control of the focused laser spot. This study achieved the optical path design of a variable focus laser searchlight and the control of the focused laser spot, and used a dichroic chip to achieve mixed white light output of blue and yellow light. The overall optical efficiency of this optical system is high, and it has strong practical significance.
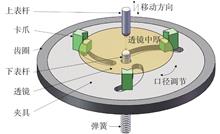
As one of the key components of an optical system, the processing quality of the lens greatly affects the performance of the optical system. The variation of the lens' center thickness has the most significant impact on the overall imaging quality of the optical system. The existing non-contact and contact measurement equipment has some shortcomings. Therefore, this paper proposes a diameter adaptive method for measuring the center thickness of a lens. Based on this method, a set of lens center thickness measurement device was designed and built. The measurement accuracy comparison and the repeatability measurement test are carried out. The results show that the error of the measurement device studied in this paper is comparable to the error of the measurement device used in the production line, which meets the detection requirements of optical lenses. The device has the advantages of simple and reliable structure, convenient operation, high measurement accuracy, and saving the production cost of optical lenses, and has been used in production lines.
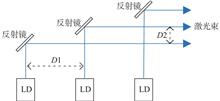
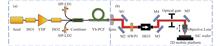
A 783 nm femtosecond fiber laser with long repetition rate was designed and constructed. The laser was based on the amplifying loop mirror mode-locked erbium-doped fiber oscillator and the environment-stable erbium-doped fiber double-stage amplifier cascaded by pulse separator. An average power of 1.3 W, pulse width of 130 fs, repetition rate of 77.1 MHz, and 1560 nm pulse output are achieved. By frequency doubling using periodically poled lithium-niobate , an average power of 0.5 W, a pulse width of 140 fs and a pulse output of 783 nm were obtained. Furthermore, the repetition frequency of erbium-doped fiber oscillator was traced to the rubidium atomic clock by repetition frequency monitoring and phase-locked loop technology. The peak value of frequency jitter is 5 mHz and the standard deviation is 1.2 mHz within 12 hours. The laser system has the characteristics of high stability, high integration and small volume.
In order to realize high-speed cutting of silicon carbide (SiC) wafers, stealth dicing experiments were carried out by using self-developed high-energy picosecond pulsed fiber lasers. According to the cross-section topography, surface thermal damage area and edge straightness of the slices, cutting results of the picosecond lasers were analyzed, and the effects of single pulse energy and scanning speed on the slice quality were explored. The results showed that when a picosecond laser with center wavelength of 1030 nm, repetition rate of 100 kHz, pulse energy of 20 μJ, and pulse width of about 100 ps was used for stealth dicing of a SiC wafer with thickness of 360 μm. The quality of the slices can meet the requirements of practical applications. The scanning speed can reach 400 mm/s and the corresponding cutting speed was 44.44 mm/s, which was higher than other related reports.
In order to manage and control the existing time transmission system and ensure the flexibility, completeness, safety and high availability of the system, this paper designs a complete set of optical fiber time transmission monitoring system. A centralized structure is adopted in the system structure. In terms of functions, it includes five parts: fault management, performance management, configuration management, safety management, and data storage management. The specific implementation methods of each function are explained in detail. The system centralizes management and decentralizes control of each time transmission node at the monitoring node, and stores the data in the database. Finally, a monitoring system is tested on the point-to-point time transmission system based on BTDM-SFSW. Experiments show that the system can monitor the system in real time and deal with faults to a certain extent, which has high reliability.
In order to solve the problem of communication between the ground and the aircraft, which is called “black barrier”, the vertically polarized terahertz wave is used to realize communication. Using the discharge device to generate plasma to simulate the plasma sheath on the surface of the aircraft, and an all-fiber coupled terahertz time-domain spectrometer is used to generate 0-1 THz waves. This paper studies the transmission characteristics of vertically polarized terahertz waves in uniform non-magnetized plasma with different electron densities from an experimental point of view. The experimental results show that the greater electron density, the faster propagation speed of the vertically polarized terahertz in the plasma; as the electron density increases, the attenuation becomes smaller. This research provides an important experimental reference for realizing the communication interconnection between the ground and the aircraft.
Aiming at the problem that the heat of high-power optical devices and equipment seriously affects their stability, performance and service life, an intelligent and efficient thermoelectric cooling system based on energy feedback is proposed. Based on high precision temperature control realized by the improved incremental proportional integral differential (PID) algorithm, energy recovery mechanism isused to promote the efficiency of the thermoelectric cooler (TEC) refrigeration. Photovoltaic (PV) power management strategy is used through PC monitoring and control of the two groups of efficient storage battery charging and discharging switch. At the same time, Python+PyQt5 is used to build a visual operation graphical interface. The results show that an experimental system for circuit information monitoring and temperature efficient control of TEC device is designed and realized. This study is expected to provide a feasible cooling scheme for high-power optical devices and systems.
An apparatus for simultaneously inspecting adjacent surfaces defects of thermoelectric cooler (TEC) components based on polarization beam splitting imaging is proposed. The optical design of the apparatus for simultaneously inspecting adjacent surface defects of TEC components is discussed. The proposed apparatus employs polarization beam splitter and polarization camera and meets the conditions of equal-optical-path imaging for both top and side surfaces. The experimental investigations on defects inspection with equal-optical-path polarization imaging system are conducted. The results indicate that the proposed inspection technique with polarization splitting equal-optical-path imaging is capable of simultaneously inspecting the adjacent surfaces defects and the optical apparatus can well meet the performance requirements for inspecting adjacent surfaces defect of TEC components. The inspection resolution can reach 110 lp/mm when equal-optical-path confocal imaging is met, but the inspection resolution reduces to below 45 lp/mm when the defocus is around ±0.20mm. It was noted that the developed technique has obvious advantages of rather good imaging quality, easy adjustment of imaging system, simplified and reliable optical configurations , and improved defect inspection performance.
In order to improve the ranging accuracy, the internal timing module of the laser rangefinder is studied. The factors affecting the ranging accuracy of the laser rangefinder are analyzed. An external delay chain chip is used as the delay line to design and make a timing generator based on the field programmable gate array (FPGA) development board. The test results show that the designed timing generator can achieve 11 ps timing resolution and a maximum data rate of 600 Mbit/s, which has achieved the expected target.
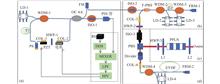
Aiming at the problems of limited measurement range, low accuracy and Abbe error in multi-degree-of-freedom measurement technology, a large-travel, high-precision, traceable, four- degree-of-freedom simultaneous measurement of heterodyne interferometry was proposed. The miniaturized 532 nm solid-state laser with iodine frequency stability was used, and the optical fiber coupling technology was used to spatially separate the dual-frequency light. Differential wavefront sensing technology realized the simultaneous detection of displacement, pitch and yaw, and wedge prisms are used to measure the change in straightness. The measuring instrument can suppress the non-linear error caused by dual-frequency optical aliasing, and realize the measurement with a travel range of 6 m, a displacement resolution of 0.13 nm, a pitch and yaw angle resolution of 0.026 μrad, and a straightness resolution of 14.88 nm. The measurement results are traceable.
Intelligent vehicles use a lidar-camera sensor fusion system to perceive the environment. Two calibration methods, feature point method and checkerboard method, are proposed for the joint calibration of different sensor coordinate systems in the data fusion. The feature-point method employs a tailored calibration template to extract several pairs of corresponding points, and solves the constraint equations for the calibration parameters in virtue of the least square method. The checkerboard method employs Zhang’s calibration method to obtain the intrinsic parameters of the camera. And then, equations are derived by using the consistency of the checkerboard plane in lidar and camera coordinate systems, solving the extrinsic parameters between the two coordinates using a linear method. The result is further refined by a nonlinear optimization method. The lidar points are projected onto the image plane by using the calibration results obtained from the two methods. Experiments demonstrate that the two methods are capable of obtaining the accurate position parameters between the coordinate systems of each sensor. The projection alignment errors are 3.03 pixels for the feature point method and 2.33 pixels for the checkerboard method.
In order to solve the fluorescence excitation problem of high throughput dPCR gene chip, a fluorescence excitation measurement and control system was designed in this paper. According to the excitation spectrum characteristics of fluorescent dyes, high-power narrow-band LED is selected as the fluorescent excitation light source and controlled by STM32 microprocessor system. The fluorescence excitation system has three fluorescence excitation channels including FAM, HEX and ROX, and the excitation power of each LED channel can be adjusted respectively. The maximum output current of the system is 8 A, the maximum output power of the single channel is 3 W, and the adjustment accuracy is less than 1.0%. The system could complete the fluorescence excitation and collection of 9 600 microdroplets of dPCR gene chip at one time. The experimental results show that the system meets the requirements of design and application.
The synthesis of nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation in liquid is a green and environmental-friendly method. Based on this method, a set of induum tin oxide ITO nanoparticles preparation system was built, which used picosecond laser as a light source to irradiate the solid target of ITO in deionized water, and finally synthesized ITO nanoparticles. With the increase of incident pulse energy and laser irradiation time, the laser ablation efficiency increased obviously and ITO production increased. The ITO nanoparticles were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). The prepared ITO nanoparticles have high purity and did not contain impurities other than Indium (In) and Tin (Sn). In addition, 72% of the ITO nanoparticles had a particle size of 20?50 nm.